- HOME
- Technical Capabilities
- Production Areas
Production Areas
Leveraging ingenious technical capabilities, bringing production system in-house
YAMADA’s manufacturing does not end just with the product --ingenious technical capabilities are displayed in every process. Other than producing over 70% of all production equipment in-house, many of the metal dies used in casting are manufactured in-house. By developing, designing, and manufacturing from production equipment to metal dies in-house, and building optimal lines for all manufacturing bases in Japan and abroad, we have developed a system that can produce high quality products efficiently. Having such a production system in-house leads to the high reliability of YAMADA products.
Production Technology Development
We utilize equipment design technology for in-house development of everything from hard to soft aspects. From small jigs to large transfer machines, the percentage of equipment made in-house is more than 70% of all our production equipment. We also make most of the dies used in different processes such as aluminum die casting and sintering. We even sell production equipment and dies throughout the world.
What is more, a broad in-house production system for production equipment and dies using the outcomes of our production technology development efforts for next-generation products also leads to improvements in product reliability, design efficiency, and productivity.
Production Technology Development System
We are constructing new technology for all-YAMADA-made sintering, aluminum die-casting, pressing, material for resin molding processes and assembly and inspection equipment. Along with the development of production technology for next-generation products, every day we are working at development to mass produce highly functional parts with high quality at a low cost using new technology.

Plastic production technology development 
Sintering production technology development 
Large die cast product straightening machine
Equipment Manufacturing System
We produce equipment for manufacturing customer-satisfying products by making high-precision, high-quality designs through proposal on optimal line configurations to manufacture highly reliable products geared toward the global market.
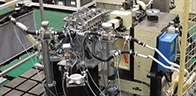
Additionally, we also manufacture equipment such as durability testing machines and performance testing machines used by our development department for in-house development. These machines contribute to our product reliability verification system.

CAD-based equipment design 
Equipment made in-house 
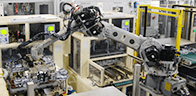
Deburring by polyarticulated robot 
Chain case automatic machining line 
Steering column assembly line 
Equipment made in-house
(performance testing machine)
Die Development
We manufacture dies, mainly for aluminum die-casting. During the design process we perform flow analysis, solidification analysis, and other analyses, the results of which are reflected in die designs. In manufacturing, we prepare CAM-based machining data and achieve high-quality, low-cost die manufacturing through machining that is as hands-free as possible, the products of which are provided worldwide.

Flow analysis
(in-die molten metal flow analysis)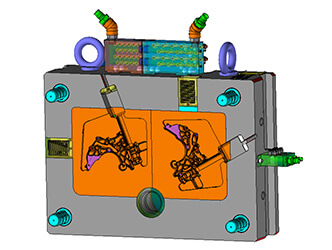
Die design
(CAD-based die design)
Product and die inspection
(measurement by camera and laser 3D measuring device)
CNC jig borer
(high-speed machining center for direct cutting of dies)
Horizontal machining center
(Used for main dies and large dies)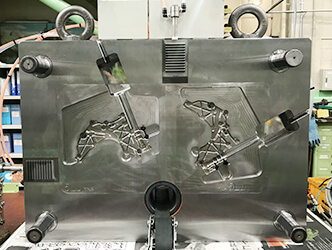
Dies made in-house
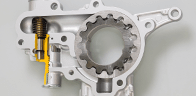
(manufacturing of products ranging from CVT parts to large oil pumps)
Production Lines
YAMADA utilizes start-to-finish production, from the material fabrication through machining to finishing, to achieve high efficiency and quality in its main functional parts through the principle of jidoka (automation with a human touch).
Casting Area
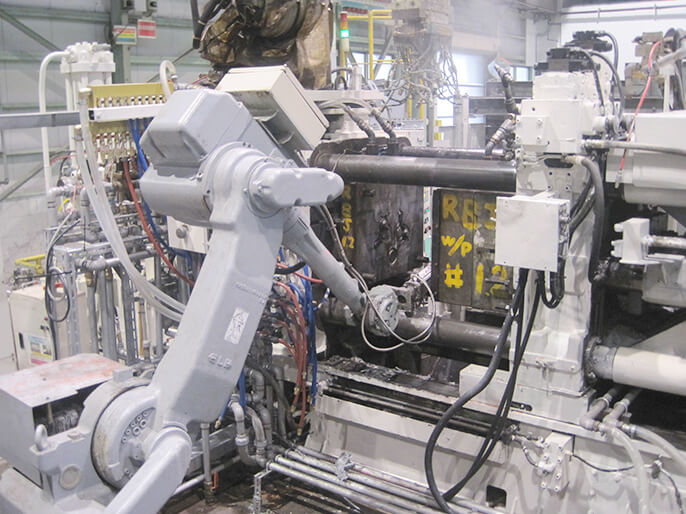
Using precision molds designed and manufactured in-house, we produce an extensive variety of thin-walled aluminum parts—which involves a high degree of difficulty—in complex shapes, from large to small parts. By leveraging the expertise of mold specifications we have acquired from mass production, and through the feedback of flow analysis and solidification analysis results we achieve quality, stable production using not only standard aluminum but also aluminum with a low flow value, which is resistant to abrasion.
Sintering (Forming, Sintering, Recompression, Machining)
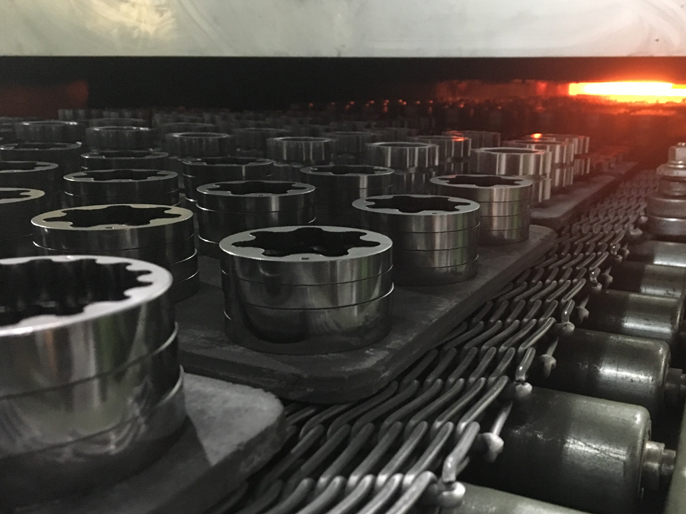

After pressing iron powder raw material into shape using a high-precision die, the formed pieces are fired at high temperature in a sintering furnace. They are then corrected in the recompression process to the customer's specified shape and finished to an even finer precision in the machining process with a CNC lathe or grinder. The Isesaki Sintering Plant develops sintered parts in-house and produces more than eight million units per year through an integrated system of from fabrication to machining.
Machining Area
Cutting
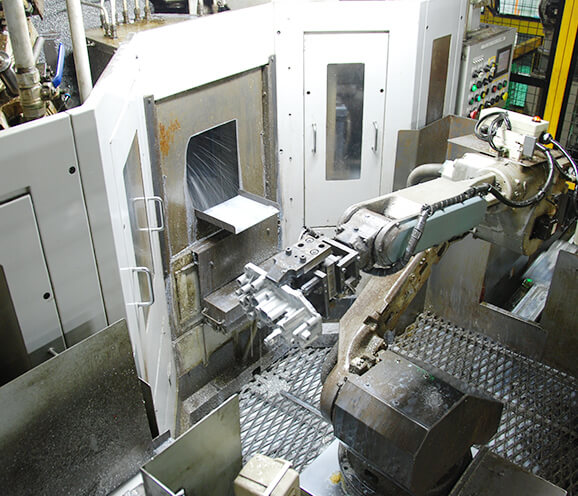

In the area of machining, we have adopted completely automatic lines fully integrated from raw material input to completion, using high-speed conveyance loaders and lane conveyors. With our original process designs, we reduce the number of personnel needed and achieve efficient, low-cost, stable production.
We operate not only high-precision cutting equipment but also diverse handwork equipment and machining technology to meet all manner of customer needs.
Induction Hardening
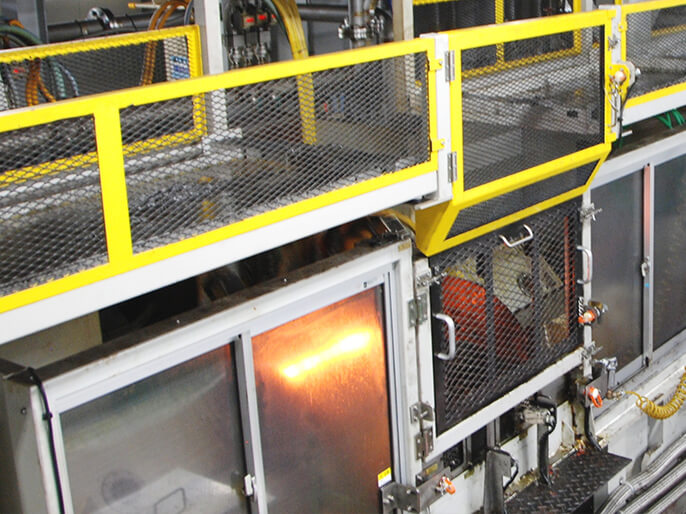

High quality is maintained by ensuring an even surface temperature and limiting curvature through the use of single shot induction hardening on the production line for intermediate shafts (half shafts). By putting this step in-line within the machining processes, we achieve highly efficient, stable production.
We also use induction hardening on the key hole in the steering wheel lock of shafts for steering columns, which improve the surface hardness of the key hole and result in improve abrasion resistance.
Forging
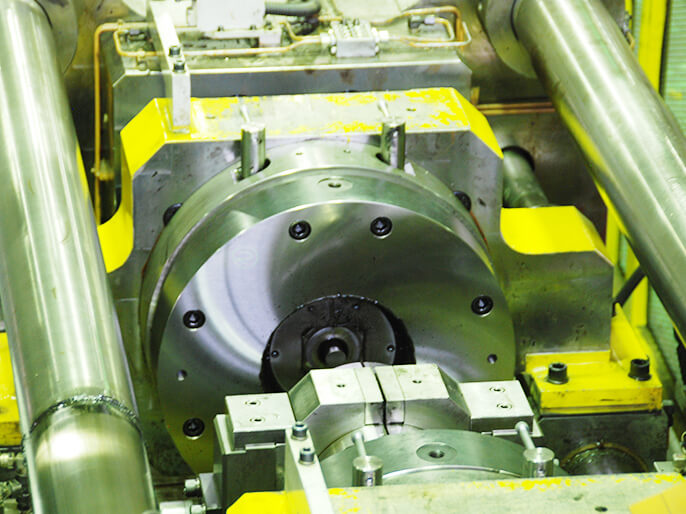
We employ cold forging in which metallic material is compression molded at room temperature using metal die. The advantage of this method is that a piece can be molded into the final shape in a short time. Since this method produces a surface finish and a high-precision part, it is possible to manufacture a shape that is close to the final product, thereby minimizing post-processing such as cutting and enabling shorter machining times.
Welding
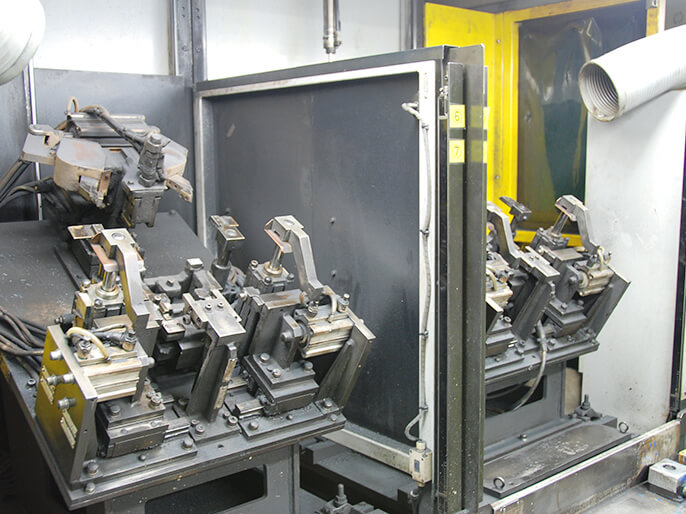

For bracket welding we have a welding line that achieves stable reproducibility and increased efficiency by aligning steering column parts produced in the press process and robotically welding them at multiple points.
In the pipe welding process, we guarantee quality conformance with a automatic pipe welding line.
In shaft welding, we eliminate the need for cleanup work by using TIG welding1 to achieving zero spatter.2 This also contributes greatly to our quality. With simplified human labor and equipment, this production line reduces waste and is environmentally friendly.
- 1TIG welding: Tungsten inert gas welding
A welding method that produces a clean weld by using a tungsten electrode and an inert gas as a shielding gas. - 2Spatter: Bits of molten granular metal-like sparks produced during welding.
Assembly Area
To efficiently provide customers with products at a low cost in a highly efficient manner, Yamada Manufacturing carries out production with the optimal combination of automatic free-flow lines and human work, assembling some six million pieces per year of our main products.
Each process is equipped with quality verification capabilities for quality assurance and to enable quality, stable mass production.
Together with achieving high efficiency, high quality, and low cost, we have equipped plants with dedicated cleanrooms to meet requests for degree of cleanliness and added other twists to line designs.